Weigh the Options: Weight Loss Methods in Fatty Liver Disease
Ysabel C. Ilagan-Ying, MD and Albert Do, MD MPH
Yale New Haven Hospital
This presentation is an excerpt from the ALF 2021 Poster Competition. This competition showcases posters and a brief video created by early career investigators from across the country on six areas of educational focus: fatty liver disease, liver cancer, liver transplantation, pediatric liver disease, rare liver disease and viral hepatitis. Participants are tasked with translating complicated medical information into a poster which can be easily understood by patients or the public. Posters are reviewed by a formal panel of judges comprised of Medical Advisory Council members, Board Members and friends of ALF to select a winner in each category.
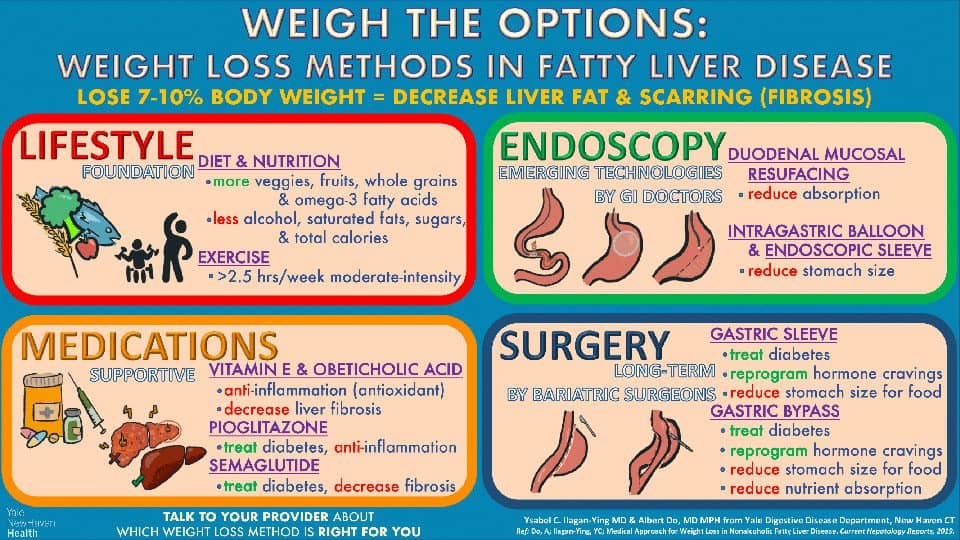
When you gain weight, your body stores extra energy in the form of fat, which can build up in your liver leading to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (or NAFLD) or in extreme circumstances, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). This fat in the liver can cause inflammation and scarring, or fibrosis, which can become severe and progress to cirrhosis.
Hands down, the most effective way to treat NAFLD is to lose weight in order to reduce fat, inflammation, and fibrosis. Research has found that losing 7-10% of their total body weight leads to improvement in fatty liver disease.
The treatments for weight loss range in cost and invasiveness. Here, we’ll review the latest researched weight loss methods in fatty liver disease. We hope this helps start your discussion with your provider about which method may be right for you!
Last updated on December 1st, 2022 at 03:40 pm