Pediatric Liver Disease

Alagille Syndrome is an inherited disorder that closely resembles other forms of liver disease seen in infants and young children.

Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is a hereditary genetic disorder which may lead to the development of lung and/or liver disease. It is the most common genetic cause of liver disease in children.

Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) and AIH/sclerosing cholangitis overlap syndrome known as autoimmune sclerosing cholangitis (ASC)

Bile ducts become inflamed and blocked soon after birth. This causes bile to remain in the liver, where it starts to destroy liver cells rapidly and cause cirrhosis, or scarring of the liver.
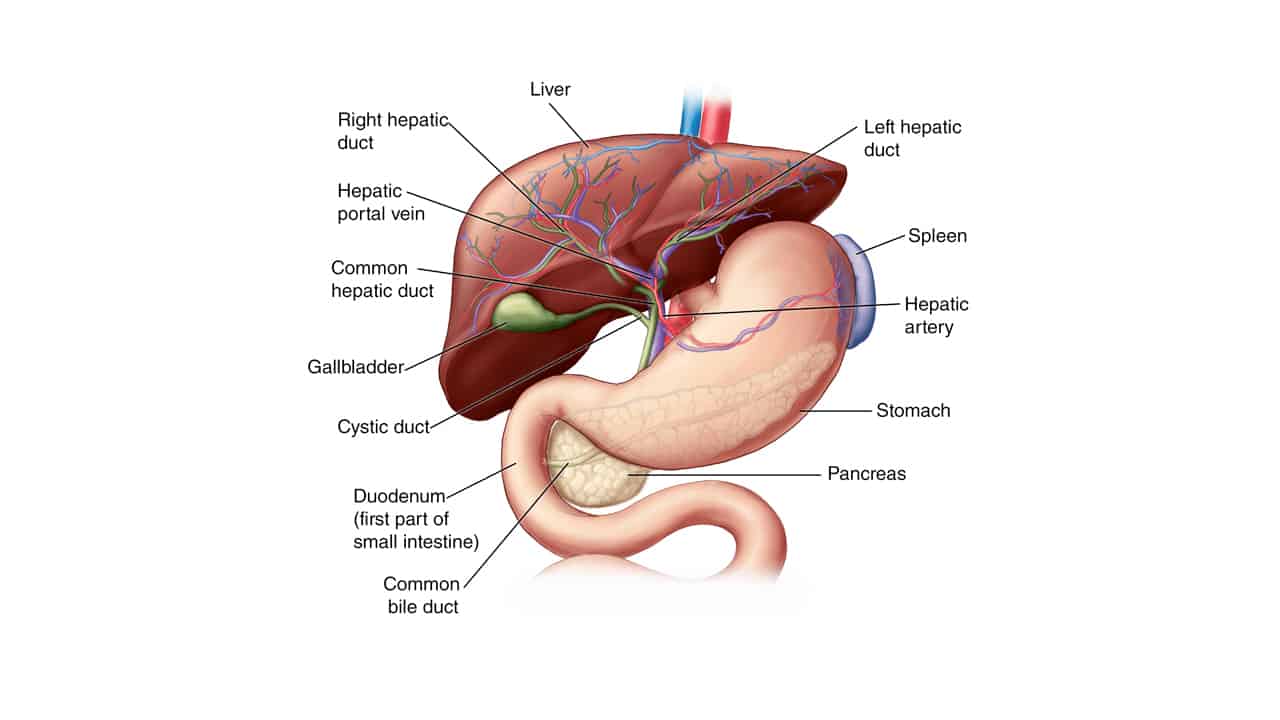
Budd-Chiari Syndrome is disorder in which veins carrying blood out of the liver become narrow and/or blocked due to blood clots.
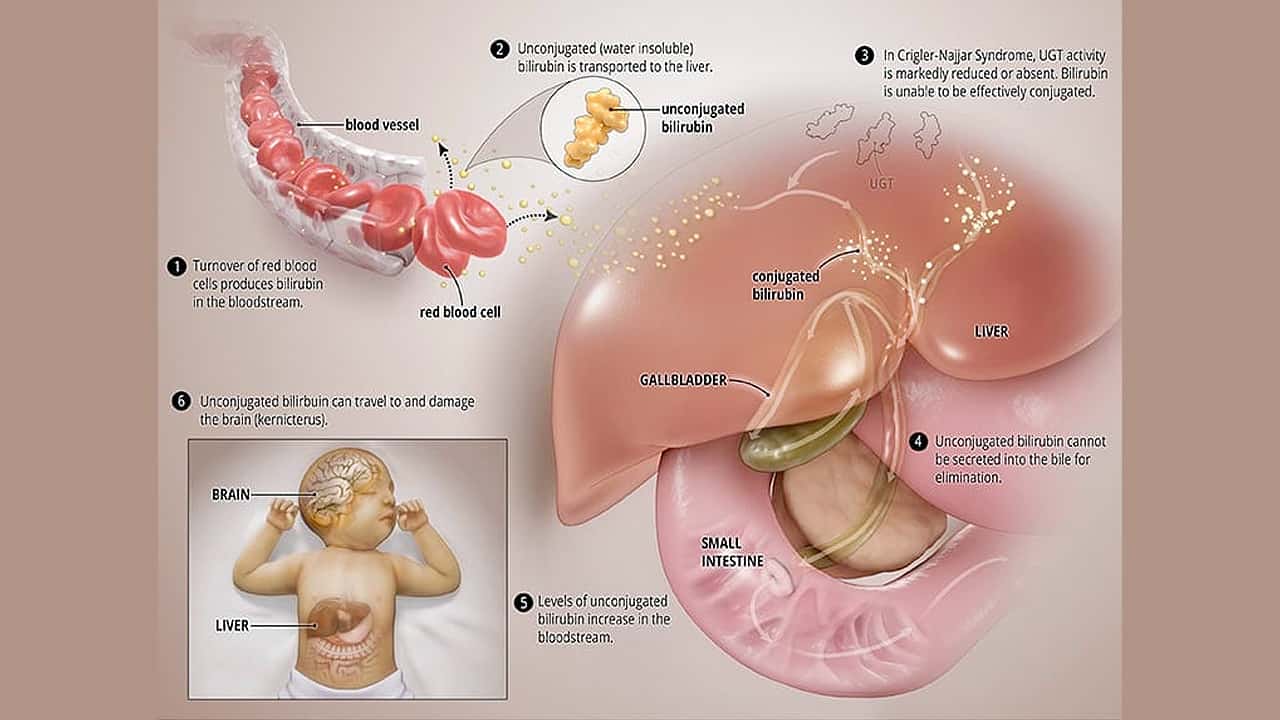
Crigler-Najjar syndrome is a rare, life-threatening inherited condition that affects the liver and is characterized by a high level of bilirubin in the blood (hyperbilirubinemia).

Galactosemia is an accumulation of galactose in the blood that can cause serious complications like an enlarged liver, kidney failure, cataracts in the eyes or brain damage.

Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis B is a virus that presents in blood and bodily fluids and causes an infection.

The hepatitis C virus, or HCV, causes an infection which damages the liver. It is spread through blood-to-blood contact with a person who is infected with the virus.

Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the most common forms of chronic liver disease in children and adolescents.

It is an inherited disorder that affects the metabolism – the way the body breaks food down into energy.

Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a chronic, or long-term, disease that slowly damages the bile ducts. Bile is a digestive liquid that is made in the liver.

Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis (PFIC) is a rare genetic (inherited) disorder that causes progressive liver disease which typically leads to liver failure.

Gilbert Syndrome is a mild genetic disorder in which the liver does not properly process a substance called bilirubin. Bilirubin is made by the break down of red blood cells.

Reye Syndrome is a rare illness that affects all bodily organs but is most harmful to the brain and the liver. It occurs primarily among children recovering from a viral infection.

Wilson Disease causes the body to retain excess copper. The liver of a person who has Wilson Disease does not release copper into bile as it should.