Home > 5 Things You Should Know About Hepatitis
5 Things You Should Know About Hepatitis
May 20, 2020
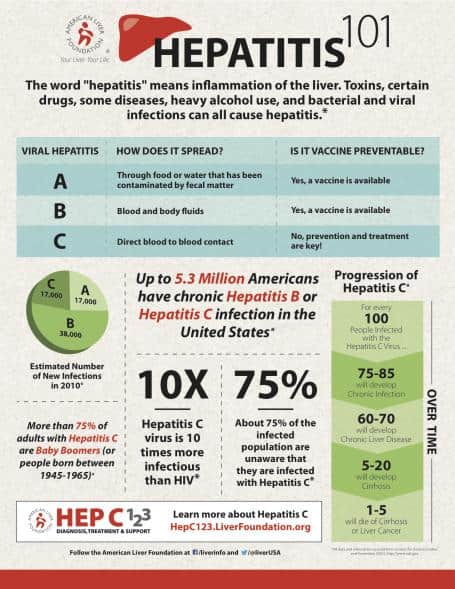
- The word ‘hepatitis’ means inflammation of the liver. Viral hepatitis is the inflammation of the liver. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
- Toxins, certain drugs, heavy alcohol use, bacterial and viral infections can all cause hepatitis.
- Hepatitis A is spread through food or water that’s been contaminated by fecal matter. There’s no treatment for hepatitis A, but routine childhood vaccination and vaccination of at risk adults are the most effective ways to reduce the disease.
- Hepatitis B is transmitted between people through contact with the blood or other body fluids (i.e. saliva, semen and vaginal fluid) of an infected person. All newborns and children should be vaccinated against hepatitis B, as well as people who are at risk.
- Hepatitis C is spread through direct blood to blood contact (i.e. sharing needles with IV drug use or having received infected blood in a blood transfusion prior to 1992). As there’s no vaccine for hepatitis C, prevention and treatment are of the utmost importance.
Get more information about hepatitis
Last updated on July 12th, 2022 at 12:53 pm