Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) and Liver Health for Veterans
Overview of Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
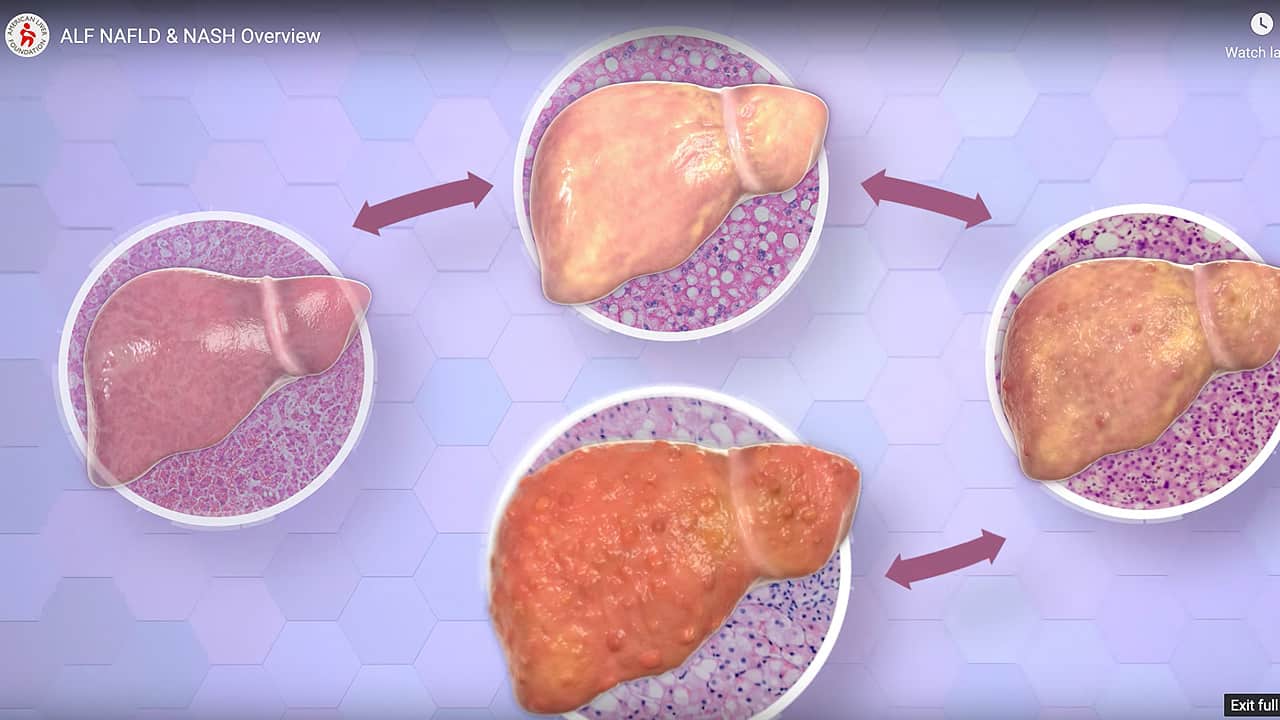
Metabolic dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), previously known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is a liver condition where excess fat accumulates in the liver without significant alcohol use. This disease can lead to inflammation, liver scarring (cirrhosis), and liver cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma, HCC) if left untreated.
MASLD Risk in Veterans
MASLD is the most common chronic liver disease in the adult US population, affecting at least 2.7 million veterans. It is a leading cause of cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and liver transplantation in veterans, and it increases the risk of developing diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and kidney disease.
Risk Factors for MASLD
The primary cause of MASLD is metabolic dysfunction. Factors such as obesity, pre-diabetes, , type 2 diabetes, and high blood pressure or cholesterol contribute to fat buildup in the liver. Additionally, lack of physical activity and poor nutrition exacerbates these conditions and increases the risk of developing MASLD. Veterans with these underlying conditions need to be especially vigilant about their liver health.
Symptoms of MASLD
People with MASLD typically do not experience symptoms initially, making it difficult for people to recognize the disease until it progresses. As the disease advances, symptoms may include fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and abdominal discomfort or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. Swelling in the abdomen or legs, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and changes in appetite can occur when the disease progresses to advanced stage of cirrhosis. Since MASLD can progress without noticeable symptoms, regular evaluation is important for veterans at risk.
Diagnosis of MASLD
If MASLD is suspected, healthcare providers may perform a series of tests to assess liver function and fat accumulation. Diagnostic methods commonly used include blood tests to measure liver enzyme levels and imaging techniques such as ultrasounds, elastography, CT scan, or MRIs to visualize fat deposits in the liver. In some cases, a liver biopsy may be necessary to determine the severity of liver damage. Early diagnosis allows for timely interventions to prevent the disease from advancing to cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Prevention of MASLD
Preventing MASLD is largely centered around making healthy lifestyle choices and knowing your Fib4 score or risk for advanced liver disease. Veterans can reduce their risk by maintaining a healthy weight, preventing or controlling diabetes, and engaging in regular physical activity. Regular exercise can help or delay pre-diabetes and diabetes, reduce liver fat, and promote overall health. Additionally, veterans should adopt a balanced diet rich in whole foods and low in unhealthy fats and sugars. Managing chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes and hypertension is essential for preventing the progression of MASLD.
Veterans who have known risk factors for MASLD, such as obesity, diabetes, or hypertension, should discuss regular screenings with their healthcare providers. Early detection is key to preventing the disease from progressing to cirrhosis or liver cancer. Lifestyle modifications, including improved nutrition and increased physical activity, and avoidance of excessive alcohol consumption can significantly reduce the risk of developing MASLD.
Treatment of MASLD
Treatment for MASLD is primarily focused on addressing the underlying metabolic issues and preventing further liver damage. For veterans with MASLD, key approaches include weight loss through diet and exercise, controlling blood sugar levels, managing blood pressure and stopping alcohol consumption. A balanced diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables is essential. Once MASLD has been diagnosed, full avoidance of alcohol is preferable to reduce the risk of disease progression. Physical activity plays a crucial role in improving diabetic risks and reducing liver fat. In some cases, medications may be prescribed.
For veterans with advanced MASLD or cirrhosis, more intensive treatments may be needed to manage liver health. These may include medications to reduce inflammation, as well as interventions to manage any complications, such as bleeding or infections. Monitoring liver health through regular screenings and medical checkups is essential to detect any signs of liver cancer or other serious issues.
Click here to download a printable infographic about MASLD for Veterans
The Liver Health for Veterans Information Center is a collaboration with the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) and Veterans Health Administration (VHA).
Related Videos
Last updated on January 12th, 2026 at 04:28 pm